Preventive Services
1. Dental Check-ups:
Regular dental check-ups, typically recommended every six months, involve a comprehensive examination by your dentist. This includes assessing the health of your teeth, gums, tongue, and other oral structures. Through these routine check-ups, potential issues can be identified early, enabling timely intervention and preventing the progression of dental problems.
2. Dental Cleanings:
Professional dental cleanings, performed by a dental hygienist or dentist, involve the removal of plaque and tartar from your teeth. Even with diligent brushing and flossing, certain areas can be challenging to clean thoroughly. Dental cleanings help prevent gum disease and cavities by ensuring that your teeth are free from the buildup of harmful bacteria.
3. Dental Sealants:
Dental sealants are thin, protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of your back teeth (molars and premolars). These areas have grooves and pits where food particles and bacteria can easily accumulate, leading to decay. Sealants act as a barrier, preventing these substances from settling in the vulnerable areas and reducing the risk of cavities.
4. Fluoride Treatments:
Fluoride is a mineral that strengthens tooth enamel, making it more resistant to decay. Fluoride treatments involve the application of a fluoride solution or gel to your teeth. This process helps remineralize areas that may have started to demineralize due to acid attacks from bacteria, contributing to the overall health and strength of your teeth.
5. Oral Cancer Screenings:
Regular oral cancer screenings are a vital component of preventive dental care. Your dentist will examine your oral tissues, including the tongue, gums, cheeks, and throat, to detect any signs of abnormalities or early indicators of oral cancer. Early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment.
6. X-rays for Diagnostic Purposes:
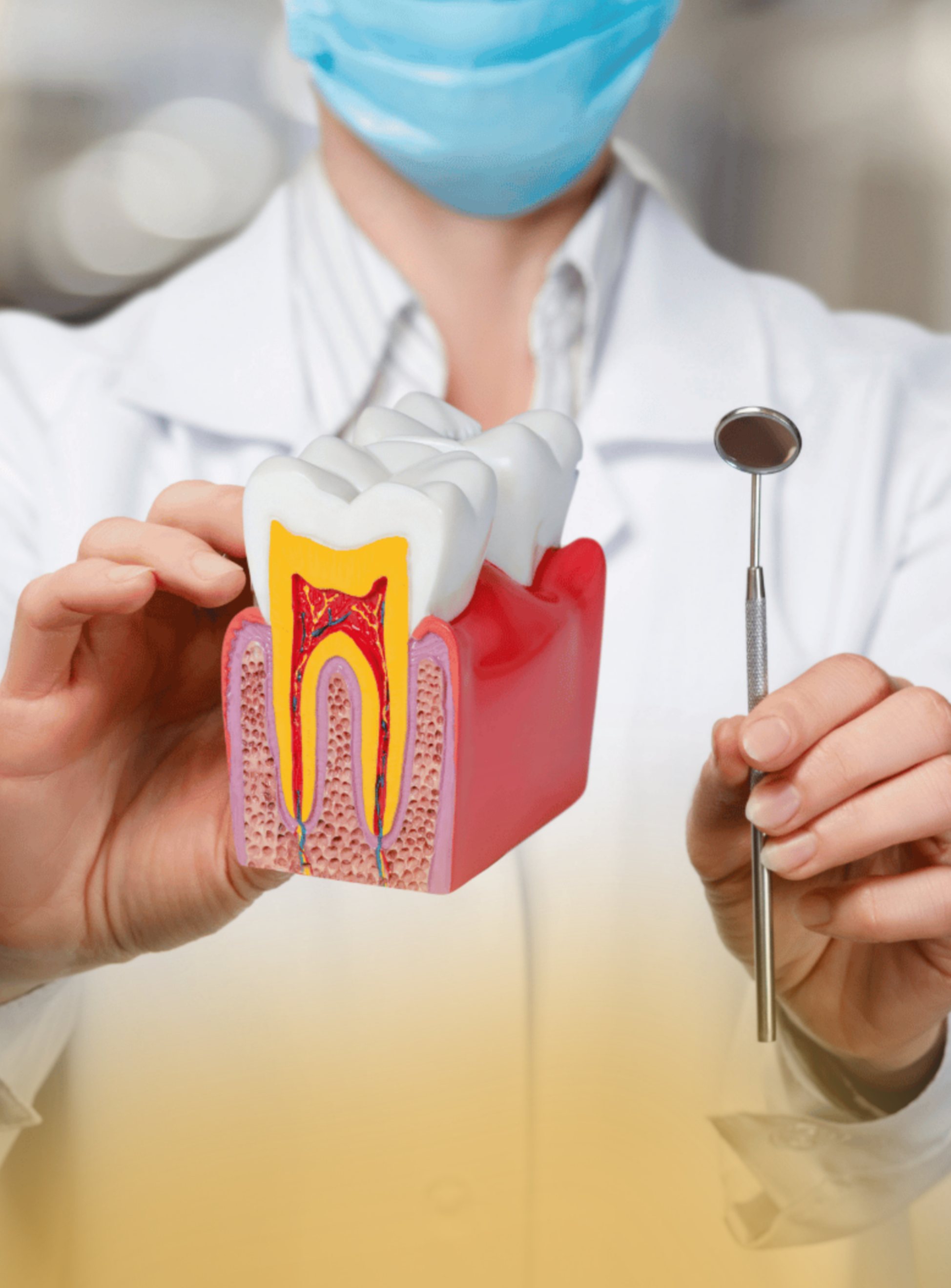
Dental X-rays are diagnostic tools that provide a detailed view of your teeth, roots, jawbone, and oral structures that are not visible during a regular examination. They help dentists identify issues such as cavities between teeth, impacted teeth, jawbone problems, and abnormalities in tooth roots. X-rays play a crucial role in creating a comprehensive picture of your oral health, guiding treatment plans effectively.
FAQ
Healing times vary, but it typically takes a few weeks. Follow post-extraction care instructions provided by your dentist to promote optimal healing.
Stick to soft, cool foods initially, gradually progressing to a normal diet. Avoid hot or spicy foods, and refrain from using a straw, as suction can disrupt the healing process.
Over-the-counter pain relievers and applying an ice pack to the affected area can help alleviate discomfort. Follow your dentist's recommendations for pain management.
Mild oozing is common initially. Bite on a gauze pad provided by your dentist to control bleeding. If bleeding persists, contact your dentist for guidance.
Resume gentle brushing and flossing in the surrounding areas 24 hours after extraction. Be cautious around the extraction site to avoid irritation.
Yes, it's common to feel drowsy or disoriented for a few hours after dental anesthesia. Avoid operating heavy machinery or making important decisions during this time.
Common side effects include temporary numbness, dizziness, or nausea. Serious complications are rare but can include allergic reactions. Inform your dentist of any concerns or unusual reactions
The duration of dental anesthesia varies depending on the type used. Local anesthesia typically lasts a few hours, while general anesthesia can have lingering effects for several hours after the procedure.
Your dentist will provide specific instructions regarding fasting before the procedure. Generally, it's recommended to avoid eating or drinking for a certain period before anesthesia to reduce the risk of complications.
Amalgam fillings are made of a mixture of metals, including mercury, while composite fillings are tooth-colored and composed of a resin material. The choice between them depends on factors like location, size of the cavity, and aesthetic preferences.